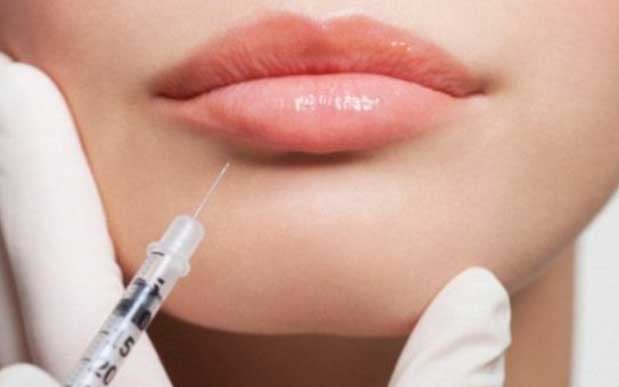
Study reveals alarming dangers of anti-ageing jabs
Paralyzing toxins inside Botox can travel to other parts of your body, an alarming new study reveals.
The age-defying injection was approved by the FDA in 2002 on the grounds that its muscle-freezing chemicals would not move from the injection site.
In 2009, the FDA warned that there was tentative research showing botulinum toxin - the active ingredient - could spread further than the targeted cell.
But now, a team at the University of Wisconsin Madison has confirmed that theory in an unprecedented set of scientific experiments. The paper, published in the journal Cell Reports, has been described as the most definitive evidence against Botox.
Botox is a brand name.
It is the most famous version of a popular injection used to hide the effects of ageing.
The active ingredient is botulinum toxin - a chemical so toxic that it has to be measured in trillionths of grams. Botulinum toxin works by temporarily paralyzing the muscles it targets, thereby smoothing wrinkles.
The effect lasts for a few months before it has to be done again.
Though the chemical was discovered in the 1800s, it was not used as an anti-ageing device until the early 2000s.
It was approved by the FDA in 2002 on the grounds that the toxins do not spread to other parts of the body.
If it did spread elsewhere, patients run the significant risk of paralysis in other parts of their body.
They may also contract a rare and incurable disease called botulism, which is normally caught from water contaminated with botulinum.
Sufferers of botulism lose control of their facial muscles, making it near impossible to swallow or breathe.
There has been mounting evidence to show that Botox might not be as controllable as once believed.
The new study by University of Wisconsin Madison provides damning evidence against the toxin.
It will reignite fears that the boosters could have more crippling long-term health effects than the industry acknowledges.
According to lead author Edwin Chapman, professor of neuroscience at the University of Wisconsin Madison, this research unequivocally showed a widespread effect.
′Every time one fraction of the toxin acts locally (on the first nerve cell it contacts), another fraction acts at a distance,′ Chapman explained.
′It′s unknown how far they travel, which likely depends on the dose of toxin and other factors.′
Botulinum toxins were first discovered in the 1800s.
It is the strongest agent in Botox Cosmetics, the popular no-fuss alternative to cosmetic surgery.
After 13 years on the market, Allergan PLC, which provides four versions of botulinum toxin, reported global Botox sales of nearly $2 billion in 2015.
Unlike most procedures, Botox does not require any recovery time and takes just a few minutes to administer.
The formula is injected into the face at different points to tighten the muscles and reduce wrinkles, thereby hiding the effects of ageing.
It works by blocking the nerve signals that tell your face muscles to contract.
This temporarily paralyzes the muscles and smooths wrinkles for a few months before another dose is needed.
The chemical is so powerful it is measured in trillionths of grams.
The study looked at mouse neurons in wells connected by tiny channels that allow growth of axons - the long fibers that neurons use to communicate.
In tests of two botulinum toxins, the researchers saw toxin molecules entering the injected cell, as expected.
Once inside a neuron, botulinum toxin splits proteins responsible for fusing of chemical containers.
Normally chemical signals tell muscles to move.
Cutting communication between neurons and muscles leads to temporary paralysis of the target site.
But Chapman′s group captured microscopic images that showed toxin molecules were moving to nerve cells that had not initially received the harmful molecules.
Related News

Women found to appear up to 20 years younger if they stay out of the sun

Correlation Between Almonds and Weight Gain

5 Tips to Take Care of Your Sensitive Skin

How mood and eating behaviour are connected

10 Benefits Of Climbing Stairs ? An Underdog In The World Of Fitness

5 Reasons Cheese is Actually Good For Your Health

The Beauty Benefits of Exercise

Smoking and sight loss warning
Most Read
★Why You Probably Shouldnt Take Diet Advice from Your CrossFit Coach
★Top 5 foods for glowing skin
★5 foods for healthy skin
★Plum goodness for your hair!
★Everyday Medications You Should Never Take When You Exercise
★5 surprising beauty benefits of amla
★Legumes, nuts and kale can help you get big muscles
★Hard work, no pay linked to mental health issues in comedians
★Cooking in aluminium pans may be dangerous for your health
★Humans evolved to benefit from fermented foods
★The best skin care quickies men with oily skin can get
★5 Dairy-Free Cheese Options Worth Trying
★4 Totally avoidable gym mistakes
★How to Set Weight-Loss Goals You Can Actually Achieve
★Just ten minutes of play a day can help children reduce their risk of developing heart disease and diabetes later in life
★Take care of your coloured hair with Wella
★Five foods that can cause problems if consumed on an empty stomach!
★9 Simple Yoga Asanas & Tips for Weight Loss
★Yoga Heals More than Just Your Body
★Making handloom accessible
★Scientists found effective dandruff treatment
★Top 3 Core Exercises While Pregnant
★10 Natural beauty tips for face you must try
★5 Exercises to Reduce Belly Fat
★7 Healthy Hacks for Your Pumpkin Spice Latte
★Surgery addict rushed to hospital after his body REJECTED his new nose
★Guinness World Record for bearded woman Harnaam Kaur
★Natural Herbal Gummies
★Exercise can help boost memory through bone hormone: Study
★Can high heels give you cancer?
★6 Foods You Can Incorporate In Your Fat Burner Diet For Best Results
★Looking towards India for design
★Pasta eaters may have better diet quality: study
★Cancer risk of breast implants 10 times higher than first feared
★Tips to Even your Skin Tone Naturally
★10 Surprising Things That Can Cause You to Lose Muscle
★8 Practical Tips to Lose Weight Without Dieting
★Do you want to be paid for sleeping well at night?
★Eat more fruit and veg for a longer life
★Why and how exercises reduce the risk of CANCER?
★Cancer warning over skin bleaching treatment
★5 most surprising cosmetic surgery trends across the globe
★Dandelion Benefits Biodiversity, Soil and Your Health
★5 Common Mistakes that May Ruin Your Skin
★Vitamin reverses aging in organs and muscles
★How to Make Elderberry Syrup
★Could laser hair removal give you CANCER?
★Best and Worst Drinks for Weight Loss
★12 Benefits of Hair Spa Treatment
★Why You Need to Start Combining Avocados and Peaches
